
School of Medicine
The NYMC School of Medicine is one of the oldest and largest medical schools in the U.S., dating back to 1860. Since then, the School of Medicine has grown in reputation while it remains a trailblazer and focused on training the next generation of physicians to provide compassionate, competent medical care.
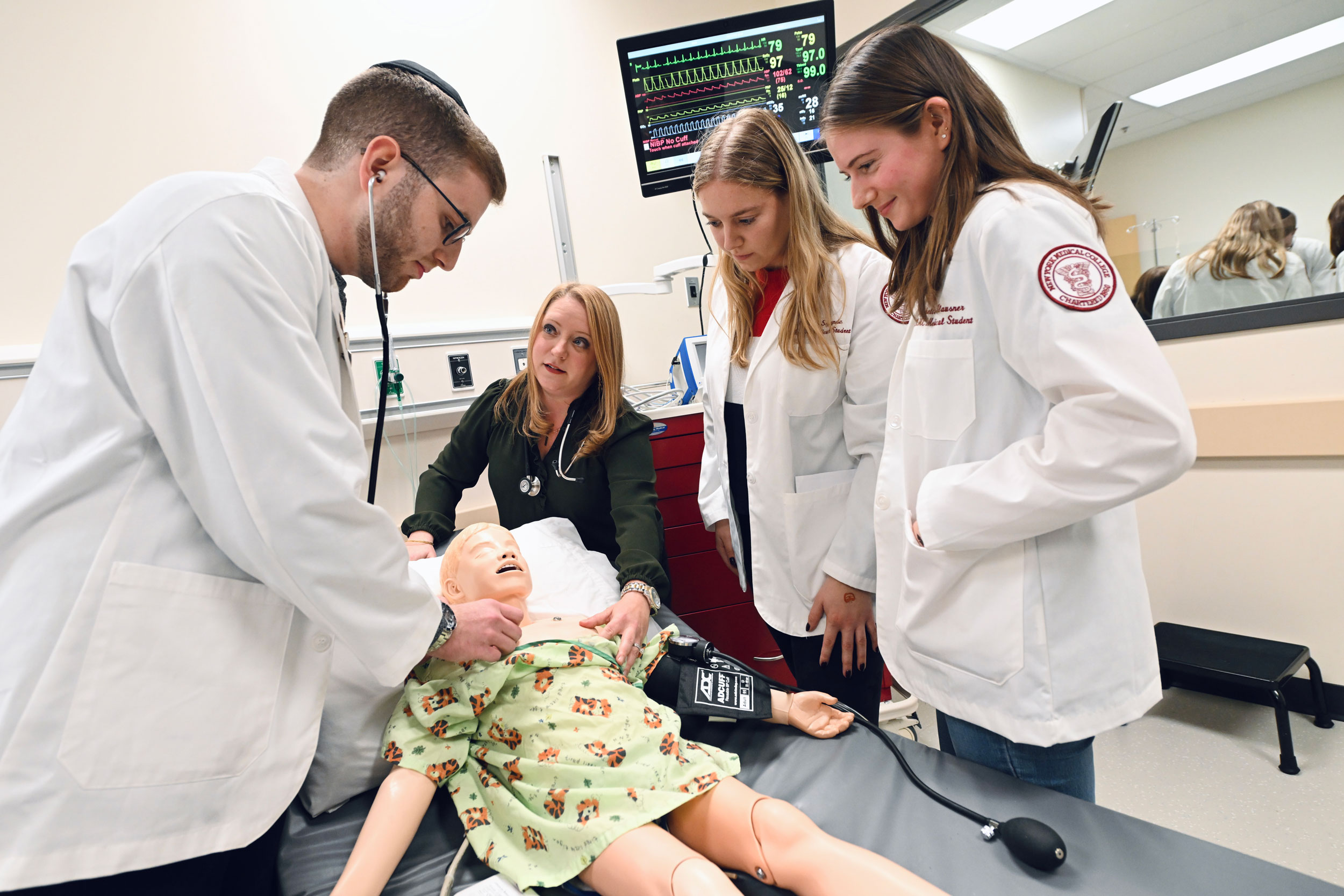
Today, we enroll approximately 200 students each year, employ a faculty of approximately 1,700 and offer three degree tracks: M.D., M.D./M.P.H. and M.D.-Ph.D.
At the School of Medicine, you’ll go through rigorous medical training, interact with patients in diverse clinical settings and have a direct impact on the community. Your education at the School of Medicine will prepare you to match at some of the strongest residency programs in the country.
M.D. Program Highlights

In the School of Medicine, you will have the opportunity to gain firsthand experience working with real patients in more than 30 clinical sites, including major medical centers, community hospitals, and ambulatory centers. You will enjoy an active campus life, with more than 100 student clubs and organizations on a suburban campus just minutes from New York City. Our supportive community and extensive academic support and mentorship network will help you navigate the challenges of med school. You’ll learn from a diverse group of peers and medical professionals and have access to both the excellent resources of the School of Medicine and the facilities, centers, and faculty that come with a college spanning so many clinical and research disciplines.
Quick Facts

30+ Affiliated Clinical Sites
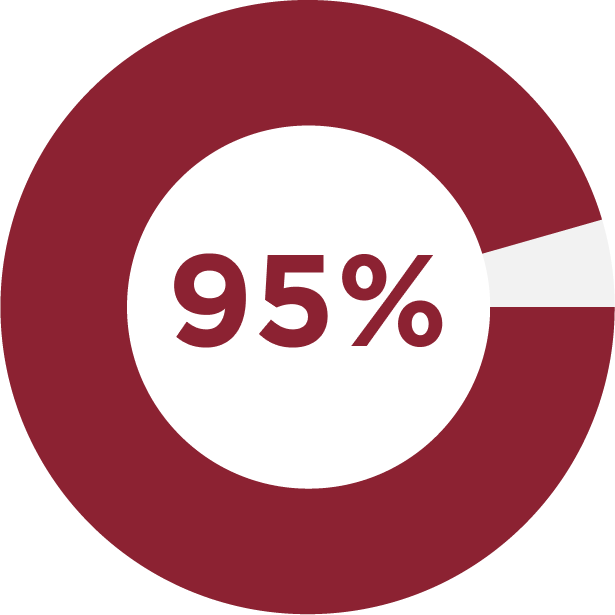
95% Average Step 1 Licensing Exam Pass Rate (over three years)
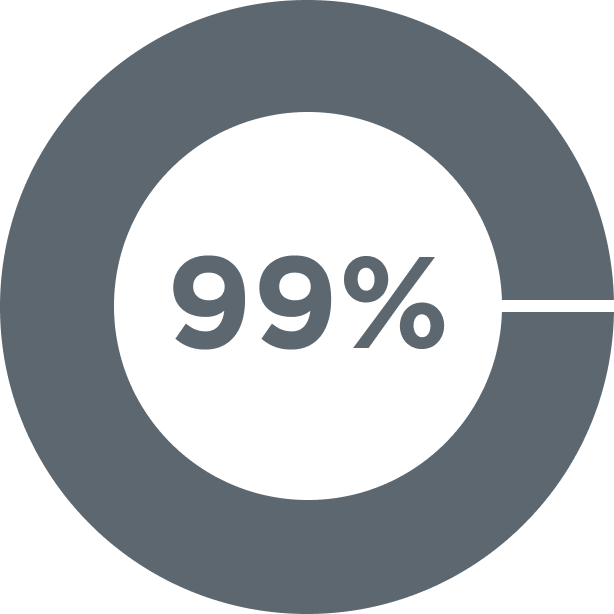
99% Average Residency Match Rate
Upcoming SOM Events
Jul 16Wednesday, July 16, 2025, 8:30 - 10am ETVisiting Professor Trauma Rounds
Department of Surgery
Jul 21Monday, July 21 - Friday, July 25, 2025 ETSOM Class of 2029 TTMS
School of Medicine
Jul 24Thursday, July 24, 2025, 3:30 - 4:30pm ETSOM Class of 2029 Parents and Partners Orientation
School of Medicine
Jul 24Thursday, July 24, 2025, 4:30 - 6:30pm ETSOM Class of 2029 Dean's BBQ
School of Medicine
“Our dynamic integrated curriculum graduates exceptional, self-directed, and compassionate physician leaders dedicated to the health and wellness of all people and communities.”
Pamela Ludmer, M.D., M.M.E.L.
Dean for Undergraduate Medical Education
What Sets SOM Apart
[AUDIO DESCRIPTION] Logo: New York Medical College, A Member of Touro University. School of Medicine
Neil W. Schluger, M.D. -- Dean; Professor, Medicine; School of Medicine
[Neil Schluger] At the New York Medical College School of Medicine, we're educating the next generation of physicians to work with the most sophisticated, advanced tools of science and medicine, but in a manner that's caring, compassionate, and that shows concern for patients from all walks of life.
[MUSIC PLAYING]
[AUDIO DESCRIPTION] Ricardo, Class of 2026, School of Medicine
[Ricardo] There was a school that believed in me before I was able to believe in myself.
[AUDIO DESCRIPTION] From above, brick buildings stand among mature trees and a plush lawn.
[Neil Schluger] New York Medical College is located on a beautiful campus in Valhalla, New York, in Westchester County. It's a stone's throw from New York City. You can hop on the train and be in the middle of Manhattan in 35 minutes.
[MUSIC PLAYING]
[AUDIO DESCRIPTION] Students wearing white coats speak outside.
[Jared] Having New York City right nearby is game changing.
[Neil Schluger] Our campus really provides our students with the opportunity to be part of a community.
[Deepika] Student life is very vibrant here. There's a whole bunch of clubs to get involved.
[MUSIC PLAYING]
[AUDIO DESCRIPTION] Jared, Class of 2027, School of Medicine
[Jared] Having that on-campus housing is really good for the social connection as well as just building that tight knit community.
[MUSIC PLAYING]
[AUDIO DESCRIPTION] Mill Etienne, M.D. '02, M P H, F A A N, F A E S -- Vice Chancellor for Diversity and Inclusion; Associate Dean for Student Affairs; Associate Professor, Neurology; Associate Professor, Medicine, School of Medicine
[Mill Etienne] They've got a very supportive environment for the students, faculty who are heavily engaged and seeing that the students succeed.
[MUSIC PLAYING]
[AUDIO DESCRIPTION] Students wearing white coats meet in a lab. They sit in a circle and talk with faculty.
[Jared] It's a very collaborative community as well, where it seems like everybody here, including the students, your peers, the faculty, all want to really see you succeed, and I've really seen that.
[Pamela Ludmer] We actually start teaching students how to be part of a medical team from the very beginning of medical school.
[Neil Schluger] In our redesigned curriculum, we've integrated early clinical exposure into the teaching of biochemistry, physiology, cell biology, and genetics.
[MUSIC PLAYING]
[AUDIO DESCRIPTION] Pamela I. Ludmer, M.D., M.S., M.M.E.L. -- Dean, Undergraduate Medical Education; Assistant Professor of Medicine and Pediatrics, School of Medicine
[Pamela Ludmer] All of our courses have clinical faculty and basic science faculty working together to create the content. They haven't just learned in a book and memorized material. They've learned about what this means for a patient.
[MUSIC PLAYING]
[AUDIO DESCRIPTION] Faculty demonstrates on a mannequin.
[Student] Auscultate before you palpate.
[Pamela Ludmer] Students, as soon as they come, they start to have experiences at the Clinical Skills Center with standardized patients.
[MUSIC PLAYING]
[AUDIO DESCRIPTION] Ricardo speaks with a patient in an exam room.
[Ricardo] Have you been sick recently?
[MUSIC PLAYING]
[AUDIO DESCRIPTION] Katharine Yamulla, M.H.E.A., CHSE -- Director of Clinical Skills and Simulation Center; Assistant Dean for Clinical Skills Education and Assessment, School of Medicine
[Katharine Yamulla] Here at the Clinical Skills and Simulation Center, we bring clinical learning to life. They get to be the doctor in charge. Partnering with our standardized patients and our mannequins and more than 500 task trainers, they can actually do the procedures. They can talk to the patient and diagnose them. But at the end of the day, we step out of character and we can give them holistic and quality feedback.
[Pamela Ludmer] Our students start their clerkships in April of their second year. After phase 2 of the curriculum, they go into an advanced practice phase. That's where they're acting as if they were an intern on the floor. They're going into the intensive care unit. They're going into the emergency room.
[Neil Schluger] We have a wide network of clinical affiliates, and the range of clinical affiliates allows our students to have a broad experience in their clinical rotations.
[MUSIC PLAYING]
[AUDIO DESCRIPTION] Edward C. Halperin, M.D., M.A. -- Chancellor and Chief Executive Officer; Professor, Radiation Medicine and Pediatrics, School of Medicine
[Edward Halperin] Our principal teaching hospitals have included the Metropolitan Hospital, Westchester Medical Center, the Hudson Valley VA, and many other hospitals which serve a diverse community.
[Neil Schluger] Sharing the campus with Westchester Medical Center allows us to work very easily with one of our really important clinical partners. The Maria Fareri Children's Hospital is also on our campus.
[MUSIC PLAYING]
[AUDIO DESCRIPTION] Deepika, Class of 2027, School of Medicine
[Deepika] There are doctors of every specialty in the hospital, so there's a whole bunch of shadowing opportunities.
[Ricardo] I've done four different rotations at different sites, including Lincoln Hospital down in the Bronx. I am originally from Brooklyn, New York, so being in a city hospital, it feels like I'm helping my own community.
[Mill Etienne] Our student body is very diverse.
[MUSIC PLAYING]
[AUDIO DESCRIPTION] Male and female students of different ethnicities meet in a lab. One of the students wears a hijab.
[Mill Etienne] It's one of the most diverse student bodies at a medical school in the United States.
[Edward Halperin] The School of Medicine, founded in 1860 by William Cullen Bryant, has a particular history of being a bastion against bigotry in health science education, being open to women, African-Americans, Italian Roman Catholics, and Jews well before other schools in the United States did so.
[Mill Etienne] New York Medical College does have numerous scholarships. I was fortunate that I was able to get the Paul and Daisy Soros Fellowship, which actually financed my first three years of medical school.
[Ricardo] I was able to receive a scholarship through a linkage program, and it's really been helpful in terms of the cost of medical school.
[Edward Halperin] We are also very proud at this college of the way we give back to the community. Our medical students work on real-time problems that affect populations in need.
[MUSIC PLAYING]
[AUDIO DESCRIPTION] Mitchell S. Cairo, M.D. -- Vice Chair and Professor, Pediatrics; Professor, Cell Biology and Anatomy, Medicine & Pathology, Microbiology and Immunology; School of Medicine, Biomedical Sciences
[Mitchell Cairo] New York Medical College is an outstanding place. We're doing a lot of cutting edge work, and this is a great place to train. There are tremendous opportunities of doing research as a student. They have an opportunity of publishing papers and presenting abstracts. We've sent students all over the world to present their research that they've done.
[Deepika] I've had the opportunity to be published multiple times, been able to go to conferences and present my work.
[MUSIC PLAYING]
[AUDIO DESCRIPTION] Dozens of students mingle in the courtyard. Some of them hold envelopes.
[Neil Schluger] Match day is always a very special day at the medical school. It's a day of great excitement. They open the envelope and find out where they're going to do their residency.
[Student] I matched at Harvard for orthopedic surgery.
[Neil Schluger] We know from long experience that our students are going to match very well and are going to enter training programs at leading institutions throughout the United States.
[Student] Mount Sinai.
[Student] Mount Sinai.
[Student] This is my co-resident.
[Pamela Ludmer] We have a 99% match rate. We know that students feel very well prepared for residency.
[Ricardo] New York Medical College has really provided all the tools that I need to become an exemplary physician.
[Neil Schluger] The fact that some of the leading training programs in the country want our students, I think, is really testimony to the preparation that our students get here.
[MUSIC PLAYING]
[AUDIO DESCRIPTION] Matched students pose for a group photo amid a burst of metallic gold confetti.
[MUSIC PLAYING]
[AUDIO DESCRIPTION] Logo: New York Medical College, A Member of Touro University. School of Medicine
[MUSIC FADES]
Latest Stories
The Academy of Medical Educators Wraps Up Successful First Year
The Cohort of Clinicians and Basic Scientists Participated in Collaborative Sessions and Undertook Projects to Enhance Their Clinical Practice and Pedagogy
NYMC Alpha Omega Alpha Chapter Receives Grant to Combat Food Insecurity
Through a Peer-led Model, FLAME Prepares Students to Screen for Food Insecurity and Connect Patients with Local Resources
Seeking Safer Treatments for Hodgkin’s Lymphoma, Dr. Mitchell Cairo to Lead New Clinical Trial
The Clinical Trial Explores the Use of Immunotherapy to Treat the Disease with Fewer Long-term Complications
New Study Demonstrates First Successful Long-Acting Oral Drug Delivery for Schizophrenia
Weekly Oral Administration of Risperidone Kept Patients Clinically Stable, Validating a Regimen That Could Transform Daily Medications into Weekly Doses

